| #13 Theoretical study of MRI artifacts by dental alloy |
||
| H.Samejima1, Y. Tegawa2, Y. Kinouchi3, and M. Akutagawa3 | ||
| 1 Graduate School of Advanced Technology and Science, The University of Tokushima, 2 Institute of Health Sciences, Graduate School, The University of Tokushima, 3 Institute of Technology and Science, Graduate School, The University of Tokushima | ||
| Introduction |
| The purpose of this study is to propose a method to calculate the metal artifact of MRI by dental alloys. The finite element method (FEM) is used widely used to calculate the magnetic field surrounding magnetic materials. Although the results by FEM fit to practical conditions, it is necessary to involve amount of time for preparation and calculation. If we have convenient, alternative, fundamental studies of MRI metal artifact expected to become simple. |
| Materials and Methods | |||||||||||||||||||||
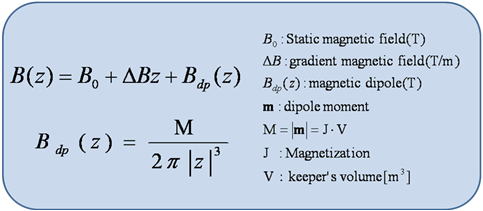
| In this study, a magnetic dipole is used as a substitution of a finite
element method. A small magnetic material in the magnetic field, such as
a magnetic keeper in MRI equipment, can be assumed as a magnetic dipole.
This analysis is only on z-axis for the understanding of the phenomenon.
Keeper's position is starting point (z=0). A magnetic field becomes strong
by a gradient magnetic field, if z is larger than z=0, and it becomes weak
if z is smaller than z=0. Fig.1 shows the parameter of the simulation. Fig.2 shows expression of magnetic induction on z axis in MRI and approximate expression of dipole |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fig.1
parameter of the simulation |
|||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Fig.2 magnetic dipole and magnetic induction on z axis | |||||||||||||||||||||
| The distortion of the image is caused by Bdp(z). Therefore, fig3 is considered as the object of examination. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||
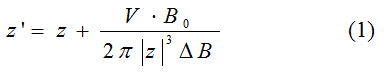 |
|||||||||
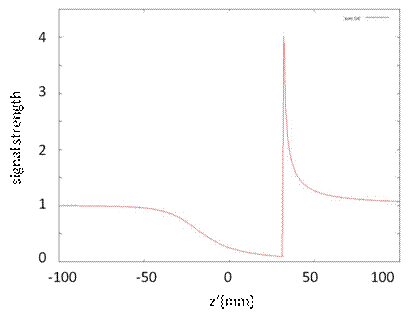
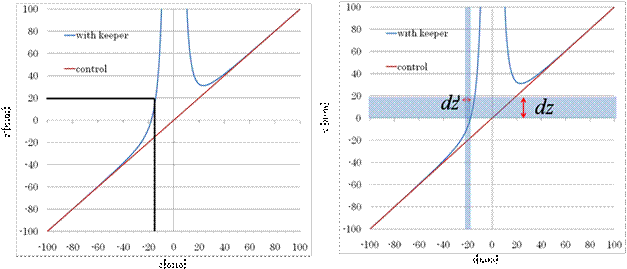
| (1) is relations of z that before and after an image reconfiguration. z’ is z position in MRI image. Fig3 is drawn by using (1). Fig.3(a) shows the example of the geometric distortion. A signal in the location of the original-18mm creates an image of it by influence of the magnetic field distortion in the location of the 20mm of a picture. Fig.3(b) shows the example of the intensity distortion A signal from the volume for the dz' is regarded as a signal from the volume for dz. That is, the strength of the signal decreases is shown. |
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Fig.3(a) geometric distortion | Fig.3(b) intensity distortion | ||||||||
| Fig.4 shows NMR signal strength on a z' axis . Fig.4 is that solved the formula (1) about z'. Since the uniform domain is assumed, signal strength must be 1 in every position, but signal strength is small around keeper. |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Conclusion |
| The MRI artifact by dental alloy contains distortion geometric and intensity
distortion. Intensity distortion is caused a decrease and an increase in
the signal strength of NMR. Geometric distortion is an error of the position
information of the signal. The result of this study shows a similar tendency as clinical studies, and it confirms that the analysis to approximate is possible. Examination in three dimensions and is future work. |
|
|
| References |
| [1]Iimuro T. Florentina : Magnetic Resonance Imaging Artifacts and
the Magnetic Attachment System Dental materials journal 13(1) pp.76-88,
126 19940625 [2]Takeyama Setsuzan : Electric magnetic phenomenon theory pp271-277, pp301-304 |